European Measure of Language Levels
Common European Framework Reference (CEFR)
Test yourself in 15 EU languages using Dialang
Contents: CEFR Levels
The A Levels: Basic User
A1 beginners:
A2 elementary:
The B Levels: Independent User
B1 Intermediate:
B2 Upper Intermediate:
The C Levels: Proficient User
C1 Advanced:
C2 Proficiency:
Common European Framework of References for Languages (CEFR): what are they? Why are they important?
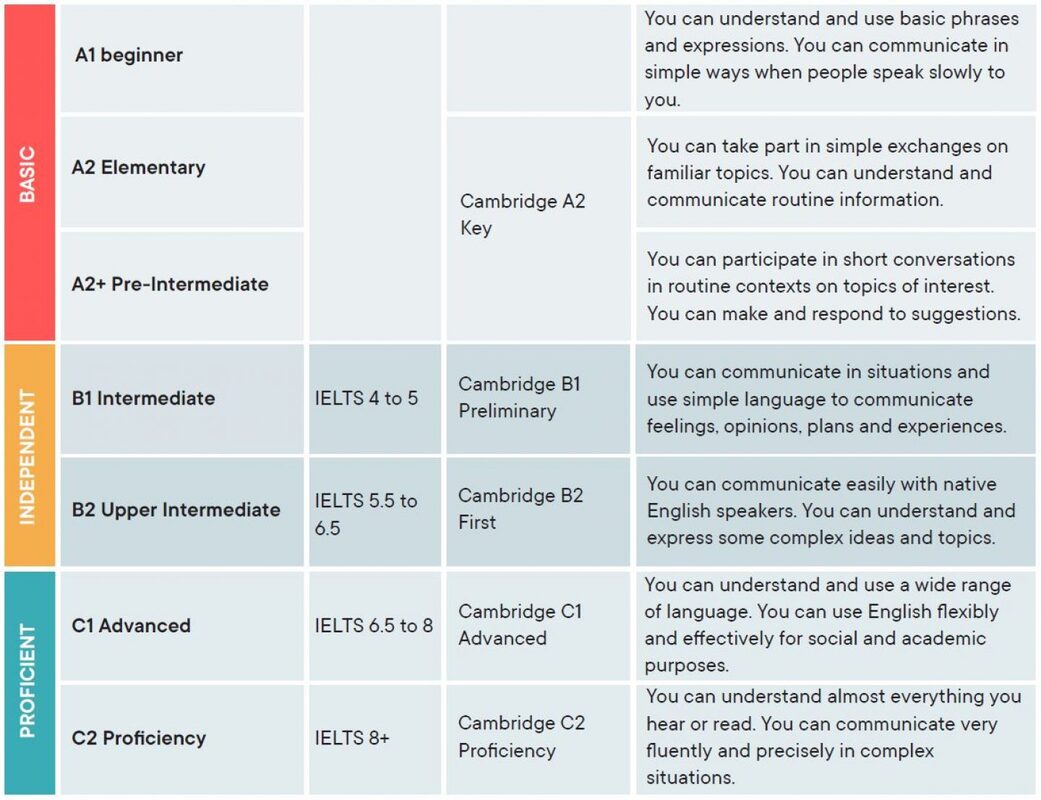
CEFR Levels
In the language-learning community in Europe, we often hear people talking about their level in the language. They can say: “I speak French at a B1 level” or “I am attending an Italian language course, I am in A2 grammar and conversation class”.
But what B1 or A2 mean?
These heading are skill levels in the Common European Framework of References for Languages system, abbreviated in English as CEFR, and they are used by language learners to measure their ability in a language. CEFR is a guideline used to describe the achievements of learners of foreign languages across Europe and, increasingly, in other countries.
CEFR was established by the Council of Europe between 1966 and 1989, it aims to provide a method of learning, teaching, and assessing which applies to all languages in Europe. In November 2001 the European Council recommended using the CEFR to set up systems of validation of language ability.
What are the Different CEFR Levels?
The six levels within the CEFR are A1, A2, B1, B2, C1, and C2. These six reference levels are widely accepted as the European standard for grading an individual’s proficiency in around forty different languages. Each level is divided into four kinds of competencies (language skills), describing what a learner is supposed to be able to do in reading, listening, speaking and writing.eady to learn?
The A Levels: Basic User
A1 beginners:
At the A1 CEFR level, a language learner:
– Can understand and use very basic expressions to satisfy concrete needs.
– Can introduce themselves and others, ask and answer questions about personal details such as where he/she lives, people they know and things they have.
– Can interact simply as long as the other person speaks slowly and clearly.
A2 elementary:
At the A2 CEFR level, a language learner:
– Can understand sentences and frequently used expressions related to areas of most intermediate areas, such as shopping, family, employment, etc.
– Can communicate in simple and routine tasks requiring a simple and direct exchange of information on familiar and routine matters.
– Can describe in simple terms aspects of their background, immediate environment, and matters in areas of immediate need.
The B Levels: Independent User
B1 Intermediate:
At the B1 CEFR level, a language learner:
– Can understand the main points of clear standard input on familiar matters regularly encountered in work, school or leisure-related topics.
– Can deal with most situations likely to arise while traveling in an area where the language is spoken.
– Can produce simple connected texts on topics that are familiar or of personal interest.
– Can describe experiences and events, dreams, hopes, and ambitions, as well as opinions or plans in brief.
B2 Upper Intermediate:
At the B2 CEFR level, a language learner:
– Can understand the main ideas of a complex text on both concrete and abstract topics, including technical discussions in their field of specialization.
– Can interact with a degree of fluency and spontaneity that makes regular interaction with native speakers quite possible without strain for either party.
– Can produce clear, detailed text on a wide range of subjects and explain a viewpoint on a topical issue giving the advantages and disadvantages of various options.
The C Levels: Proficient User
C1 Advanced:
At the C1 CEFR level, a language learner:
– Can understand a wide range of demanding, longer clauses, and recognize implicit meaning.
– Can express ideas fluently and spontaneously without much obvious searching for expressions.
– Can use language flexibly and effectively for social, academic and professional purposes.
– Can produce clear, well- structured, detailed text on complex subjects, showing controlled use of organizational patterns, connectors, and cohesive devices.
C2 Proficiency:
At the C1 CEFR level, a language learner:
– Can understand with ease virtually everything heard or read.
– Can summarize information from different spoken and written sources, reconstructing arguments and accounts in a coherent presentation.
– Can express themselves spontaneously, very fluently and precisely, differentiating finer shades of meaning even in the most complex situations.
The levels are often used casually by language learners to explain their ability at speaking, reading, writing and understanding a language. But there are also exams and certificates available to those who want to make their level official.
When do you need a CEFR levels certificates?
The CEFR is often used by employers and in academic settings.
You may need a CEFR certificate for:
– School admissions. Before you start a school course, you should test your level.
– University course requirements. To enroll in a University course in Italy you need at least a B1 level certificate.
– Employment. To work in Italy or abroad you may need from A2 to B2 level certificate, it depends on the job you are applying for.
A CEFR certificate is very useful for your CV, and they often don’t expire.
Some of your options for official examinations (or for courses with certification).
Language learners use CEFR levels for self-assessment so that they can more clearly define what they need to work on and work out, what they would like to achieve in their target language.
Is it necessary only for the professional and academic fields?
A CEFR level certificate is necessary for the professional or academic fields. Anyway, they are also very important if you want to define where you are at with your target language. If you are planning a vacation throughout Italy, for example, you may need to be at least an A2 level. This will help you to ask for a coffee, to do some shopping, to have a simple conversation with local people. CEFR levels are an important tool in a more casual language-learning environment, or if you are learning languages because you enjoy them.